
整理
Seiri
整頓
Seiton
清掃
Seiso
清潔
Seiketsu
躾
Shitsuke
5S is a visual workplace practice that comes to us from Japan.
The name comes from 5 Japanese words that start with the letter "S"
整理
Seiri
...means segregating, sorting out and getting rid of non essential items
整頓
Seiton
..means orderliness or systematic arrangement of all remaining items
清掃
Seiso
..means the act of cleaning or creating a “spic and span” workplace
清潔
Seiketsu
…means maintaining high standards of world class operational practices
躾
Shitsuke
…means the practice of self- discipline and sustaining the above
整理
Seiri
...means segregating, sorting out and getting rid of non essential items
整頓
Seiton
..means orderliness or systematic arrangement of all remaining items
清掃
Seiso
..means the act of cleaning or creating a “spic and span” workplace
清潔
Seiketsu
…means maintaining high standards of world class operational practices
躾
Shitsuke
…means the practice of self- discipline and sustaining the above
A few key benefits of 5S
Visible release of space
Significant reduction in response times leading to increased throughput
- Financial benefits
- Productivity related benefits
- Safety benefits
- Improved employee benefits
Visible release of space
Significant reduction in response times leading to increased throughput
- Financial benefits
- Productivity related benefits
- Safety benefits
- Improved employee benefits
Why is 5S important?
- 5S is the foundational input
for all Quality initiatives, be it
TPM, JIT, TQM or Six Sigma. - It is a low-investment, high
impact lean manufacturing
tool that is predicated on
people. - It engages people in “owning”
their workspace and helps to
instill a culture of quality,
productivity, and improvement.
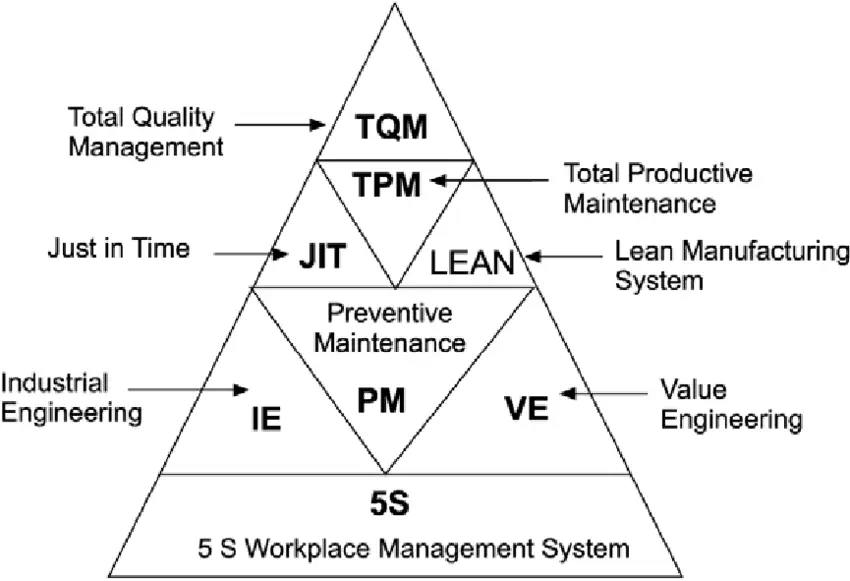
Source: https://www.researchgate.net
Know more about 5S
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ's)
What is 5S?
5S is a workplace organization method that uses five Japanese words: Seiri (Sort), Seiton (Set in Order), Seiso (Shine), Seiketsu (Standardize), and Shitsuke (Sustain). It aims to create a clean, organized, and efficient workplace.
Why is it called 5S?
The name 5S comes from the first letters of five Japanese words that describe the steps of the system. Each word starts with an “S” sound, which has been retained in the English translation.
What is the purpose of 5S?
The purpose of 5S is to improve workplace efficiency and safety by organizing and standardizing the work environment. This leads to reduced waste, improved productivity, and a safer workplace.
Who should use 5S?
5S can be used by any organization, regardless of industry. It is particularly beneficial for manufacturing, warehousing, and logistics companies, but can also be applied in offices, healthcare, and service industries.
What are the benefits of 5S?
Benefits of 5S include improved efficiency, reduced waste, better quality, enhanced safety, increased employee morale, and a more organized work environment.
How does 5S improve safety?
5S improves safety by eliminating clutter, organizing tools and materials, and creating clear pathways. This reduces the risk of accidents and injuries.
How does 5S improve productivity?
5S improves productivity by creating an organized work environment, reducing time spent searching for tools and materials, and streamlining workflows. This allows employees to focus more on value-added activities.
How can 5S reduce waste?
5S reduces waste by eliminating unnecessary items, organizing tools and materials efficiently, and improving workflow. This minimizes time spent searching for items and reduces errors and defects.
What is the relationship between 5S and Kaizen?
5S and Kaizen are both continuous improvement methodologies. 5S provides a foundation for workplace organization, while Kaizen focuses on making incremental improvements. Together, they create a culture of continuous improvement.
What is the difference between 5S and 6S?
The difference between 5S and 6S is the addition of a sixth “S” for Safety. 6S emphasizes the importance of safety in conjunction with the original 5S principles, ensuring that safety is an integral part of workplace organization.
How does 5S compare to Kaizen, TPM, TQM, Lean Tools, JIT, Gemba, Six Sigma?
- Sort: Eliminating unnecessary items to prevent accidents, maximize space utilization, and streamline workflows
- Set in Order: Strategically organizing essential items for maximum efficiency and rapid access
-
Shine: Regular cleaning and inspection that reveals equipment issues early, prevents breakdowns, and maintains workplace standards
-
Standardize: Creating clear visual systems and processes that maintain consistency across operations
-
Sustain: Building these practices into the daily culture through regular audits and continuous improvement
-
Lastly Safety: Integrating safety protocols into every aspect of workplace organization
What is the first step of 5S and what does it involve?
The first step, Sort (Seiri), involves identifying and removing unnecessary items from the workplace. This helps to eliminate clutter and make space for essential items.
How do you implement the "Set in Order" step?
“Set in Order” (Seiton) involves organizing items so they are easy to find and use. This includes labeling, creating designated storage areas, and arranging tools and materials in an efficient manner.
How do you "Standardize" in 5S?
“Standardize” (Seiketsu) means creating standard procedures and practices for maintaining the first three steps (Sort, Set in Order, and Shine). This ensures consistency and helps sustain the improvements.
What is the importance of "Sustain" in 5S?
“Sustain” (Shitsuke) is about making 5S a habit and maintaining the improvements over time. This involves regular audits, training, and continuous improvement to ensure the practices are followed consistently.
What is red-tagging in 5S?
Red-tagging is a process used during the Sort phase where items that are not needed are tagged for removal. This helps to identify and eliminate unnecessary items from the workplace.
What is a shadow board?
A shadow board is a tool used in the Set in Order phase where outlines of tools are marked on a board. This helps ensure each tool is returned to its designated spot after use, making it easy to identify missing items.
How does 5S contribute to employee engagement?
5S contributes to employee engagement by involving employees in the process of organizing their work environment, empowering them to make improvements, and recognizing their contributions. This leads to a sense of ownership and pride in their work.
How do you maintain 5S over the long term?
Maintaining 5S over the long term requires regular audits, continuous training, management support, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. It’s important to make 5S a part of the daily routine.
How do you conduct a 5S audit?
A 5S audit involves evaluating each area against established 5S standards, identifying areas for improvement, and ensuring that practices are being followed consistently. It includes using checklists and rating systems to assess compliance.
What challenges might be faced when implementing 5S?
Challenges include resistance to change, lack of commitment from leadership, insufficient training, and difficulty in sustaining the improvements. Addressing these challenges requires strong leadership and continuous engagement.
How can employees be encouraged to participate in 5S?
Encouraging participation involves providing training, involving employees in the process, recognizing and rewarding contributions, and demonstrating the benefits of 5S through real-life examples and success stories.
What role does leadership play in 5S?
Leadership plays a crucial role in 5S by providing support, resources, and commitment. Leaders must lead by example and ensure that 5S principles are integrated into the organizational culture.
What is the role of visual management in 5S?
Visual management involves using visual cues such as labels, signs, and color coding to enhance workplace organization and efficiency. It helps employees quickly identify tools, materials, and information, reducing confusion and errors.
How do you ensure sustainability of 5S practices?
Ensuring sustainability involves regular audits, continuous training, management commitment, employee involvement, and integrating 5S into daily routines and company culture. Continuous improvement efforts also play a vital role.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in 5S implementation?
Common mistakes include lack of management support, inadequate training, failure to involve employees, not conducting regular audits, and not sustaining the improvements over time. Avoiding these mistakes is key to successful implementation.
How do you measure the success of 5S?
Success can be measured through regular audits, key performance indicators (KPIs) such as productivity, quality, and safety metrics, and feedback from employees.
How long does it take to implement 5S?
The time required to implement 5S varies depending on the size and complexity of the organization. Initial implementation can take a few weeks to a few months, but sustaining 5S is an ongoing process.
Can 5S help in reducing downtime?
Yes, 5S can reduce downtime by ensuring tools and equipment are properly organized and maintained, making it easier to identify and address issues before they cause delays.
How does 5S help in reducing costs?
5S helps reduce costs by minimizing waste, reducing inventory, preventing defects, and improving efficiency. This leads to lower operational expenses and higher profitability.
How can 5S improve customer satisfaction?
5S improves customer satisfaction by enhancing product quality, reducing lead times, and ensuring on-time delivery. A well-organized workplace leads to more consistent and reliable output.
Can 5S be integrated with other improvement methodologies?
Yes, 5S can be integrated with other methodologies such as Lean, Six Sigma, Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), and Kaizen. Combining these approaches can amplify their benefits and lead to greater overall improvements.
How can technology be integrated into 5S?
Technology can be integrated into 5S through digital tools for inventory management, automated cleaning schedules, visual management software, and mobile apps for conducting audits and tracking improvements.
How can 5S be customized for different industries?
5S can be customized for different industries by tailoring the principles to the specific needs and challenges of the industry. For example, in healthcare, 5S can be used to organize medical supplies and equipment, while in manufacturing, it can streamline production processes.
Can 5S be applied outside of manufacturing?
Yes, 5S can be applied in any work environment, including offices, healthcare facilities, retail stores, and service industries. The principles of organization and efficiency are universal.
Can 5S be applied to service industries?
Yes, 5S can be applied to service industries such as hospitality, retail, and healthcare by organizing workspaces, standardizing processes, and improving service delivery. The principles are adaptable to any work environment.
Can 5S be applied to digital workspaces?
Yes, 5S principles can be applied to digital workspaces by organizing files and folders, eliminating unnecessary data, standardizing file naming conventions, and maintaining a clean and organized digital environment.
How does 5S impact environmental sustainability?
5S impacts environmental sustainability by reducing waste, optimizing resource use, and promoting recycling and efficient use of materials. It encourages practices that are environmentally friendly and resource-efficient.
What tools are used in 5S?
Common tools used in 5S include labels, shadow boards, floor markings, checklists, and visual management aids such as signs and charts.
What is the role of training in 5S implementation?
Training is crucial for 5S implementation as it ensures that employees understand the principles and techniques of 5S, know how to apply them, and are committed to maintaining them. Regular training and refreshers help sustain the 5S culture.
We'd love to have a conversation!
Please fill in the boxes below for us to reach out to you at a date and time convenient to you